L’Provincial Agency for Environmental Protection of the Autonomous Province of Trento (Appa) published the report on air quality in Trentino in 2023.
The morphology and weather-climatic characteristics of Trentino make it particularly vulnerable to the accumulation of air pollutants during the winter, when the combination of poor ventilation, limited rainfall and frequent conditions of atmospheric stability with strong temperature inversions create an environment unfavorable for the dispersion and dilution of pollutants. These conditions can lead to a persistent accumulation of harmful substances near the ground, which can last for days.
These stagnation situations not only increase the concentrations of primary pollutants, but also favor the formation of secondary pollutants, those that form through chemical-physical processes or photochemical reactions starting from primary pollutants, further worsening the quality of the air.
The interannual variability of weather and climate conditions significantly affects the average annual air qualitymaking managing air pollution a complex challenge for the province.
The state of air quality is determined thanks to the monitoring activities carried out during the year and by comparison with the data collected in previous years. Overall, the situation that emerges, according to experts, is positive, with some specific critical issues.
The nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter Pm2.5 for the fourth consecutive year have not exceeded the limit value for the annual average in all monitoring stations, and also for PM10 particulate matter, the daily limit was exceeded less than 35 times during the year (as per regulations).
Nitrogen dioxide is generated by combustion processes, is a strong oxidant and irritant and can lead to respiratory diseases. THEAtmospheric particulate matter, or fine dust (Pm10 and Pm2.5 based on the size of the dust), is essentially a set of small particles that tend to remain suspended in the air. Its anthropic sources are combustion, rubbing and erosion processes, while the natural ones are the most diverse, from desert dust to pollen, from eruptions to fires. In the case of particulate matter, the damage they can cause to human health is related to their sizebecause the smaller the particles, the greater their ability to penetrate the respiratory system and cause harmful effects both in the short term (lung irritation, bronchoconstriction, decrease in lung capacity, chronic bronchitis) and in the long term ( chronic effects, tumors).
The full compliance with safety limits it has also been observed for sulfur dioxide and benzene, as well as for heavy metals and benzo(a)pyrene.
The greatest critical issues remain for ozone: the target value, in fact, is still widely exceeded throughout the province with the sole exception of Borgo Valsugana.
Ozone is a predominantly secondary pollutant whose concentrations increase particularly in the summer seasondue to solar radiation which promotes its formation, preferentially in areas that are not intensely urbanized, such as high mountain areas.
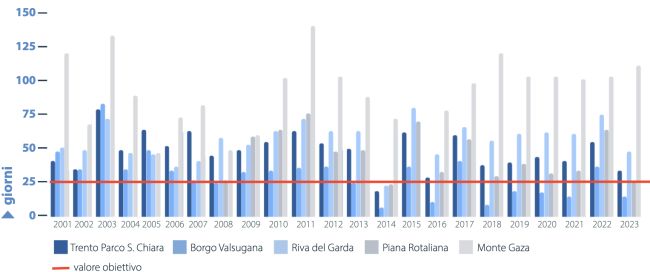
Due to its high oxidizing power, high levels of ozone pose a serious threat to human and animal health, as well as vegetation and materials. Ozone damages plants by reducing photosynthetic activity and contributing to the formation of acid rain.
As far as human health is concerned, the chronic consequences of long exposure to low concentrations of ozone are not yet fully known. However, the acute effects are well documented: severe irritation of the mucous membrane of the eyes, inflammation and alterations of the respiratory system, as well as a sensation of pressure on the chest. Particularly high concentrations of ozone can cause alterations in respiratory functions, cause an increase in asthma attacks, the onset of respiratory diseases and the worsening of pre-existing respiratory and cardiac diseases.
Interannual meteorological variability, in terms of solar radiation and temperature, plays a fundamental role in increasing ozone concentrations during the summer season and adds to the contribution of long-distance transport. As the experts who worked on the report point out, To effectively address this issue, large-scale cooperation, involving multiple nations and regions, is needed to implement targeted and coordinated strategies to reduce the impact of ozone on human health and the environment.








